Everyone’s heard of an ‘adrenaline rush.’ But what is it, really? 🤔
Let’s clear up the confusion with a story you’ll never forget. 🏠
Scene: A theft in action.
Characters: A thief and a homeowner.
If we could check their blood reports at this very moment, here’s what we’d find:
- 🥷 The Thief (High Noradrenaline/Norepinephrine): Silent, alert, and vigilant. As he enters the home, his nervous system is firing with noradrenaline. His focus sharpens, his senses heighten, and his heart beats a little faster. He’s on high alert.
- 💪 The Homeowner (High Adrenaline/Epinephrine): He hears the noise! His adrenal glands flood his body with adrenaline, converted from the initial alert signals. His heart pounds, his lungs take in more air, energy rockets to his muscles—he’s ready to face the threat or run like the wind!
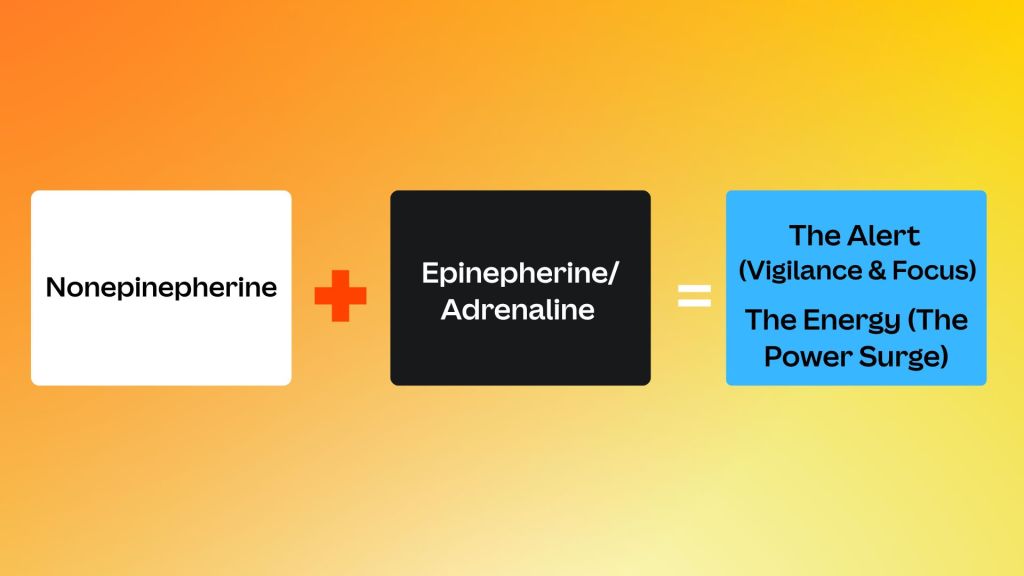
In a nutshell:
- NOREpinephrine = The Alert (Vigilance & Focus)
- EPInephrine = The Energy (The Power Surge)
🎭 The Sequel: “The Aftermath”
The owner relaxes after not hearing more noise. His adrenaline dips, and he crashes, catching up on sleep. His body struggles to dive back into the pool of homeostasis.
The thief, however, finished his job quietly, high on norepinephrine. His escape is rewarded as his brain floods with Dopamine (the joy of success) and Serotonin (the glow of satisfaction). He’s euphoric! 🎉
The Morning After (The Reality): The homeowner wakes up to survey the mess. The immediate danger is gone, but his body is now running on Cortisol—the long-term “stress hormone.” This causes the lingering anxiety, worry, and inability to fully relax after a stressful event. 😥
The Full Story Arc:
- Norepinephrine: The alert thief.
- Epinephrine: The homeowner’s powerful surge.
- Dopamine/Serotonin: The thief’s reward.
- Cortisol: The homeowner’s long-term stress.
So next time you feel that rush (or that crash afterwards), you’ll know the incredible chemical story playing out inside you!
Did this help? Share to make science relatable!
#ScienceExplained #HealthTips #MentalHealthAwareness #FightOrFlight #Adrenaline #Cortisol #StressResponse #LearnSomethingNew
For people who like to dive more into science:
Key Differences:
- Source: Norepinephrine is mainly from sympathetic neurons (and a small amount from the adrenal medulla), while epinephrine is primarily from the adrenal medulla.
- Scope: Norepinephrine’s effects are more localized (e.g., neural signaling, vasoconstriction), preparing the body for action. Epinephrine is systemic, flooding the body with energy for immediate response.
- Timing: Norepinephrine often precedes epinephrine in the stress response. For example, the brain’s locus coeruleus releases NE to heighten alertness, and if the threat escalates, the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis triggers EPI release from the adrenal glands.
- Receptor Affinity: Both bind to alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors, but norepinephrine has a higher affinity for alpha receptors (vasoconstriction, focus), while epinephrine strongly activates beta receptors (heart rate, bronchodilation, energy mobilization).
- Duration: Norepinephrine’s effects can linger in neural signaling, maintaining vigilance. Epinephrine’s effects are rapid (peak within seconds) but fade quickly (minutes) as it’s metabolized by enzymes like COMT and MAO.
